Attention
You can now run different PHP versions per project:
Release v3.0.0-beta-0.1 ![]()
Setup WordPress¶
This example will use git to install WordPress from within the Devilbox PHP container.
After completing the below listed steps, you will have a working WordPress setup ready to be served via http and https.
See also
Table of Contents
Overview¶
The following configuration will be used:
| Project name | VirtualHost directory | Database | TLD_SUFFIX | Project URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| my-wp | /shared/httpd/my-wp | my_wp | loc | http://my-wp.loc https://my-wp.loc |
Note
- Inside the Devilbox PHP container, projects are always in
/shared/httpd/. - On your host operating system, projects are by default in
./data/www/inside the Devilbox git directory. This path can be changed via HOST_PATH_HTTPD_DATADIR.
Walk through¶
It will be ready in seven simple steps:
- Enter the PHP container
- Create a new VirtualHost directory
- Download WordPress via
git - Symlink webroot directory
- Add MySQL database
- Setup DNS record
- Visit http://my-wp.loc in your browser
1. Enter the PHP container¶
All work will be done inside the PHP container as it provides you with all required command line tools.
Navigate to the Devilbox git directory and execute shell.sh (or shell.bat on Windows) to
enter the running PHP container.
host> ./shell.sh
2. Create new vhost directory¶
The vhost directory defines the name under which your project will be available.
( <vhost dir>.TLD_SUFFIX will be the final URL ).
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd $ mkdir my-wp
See also
3. Download WordPress via git¶
Navigate into your newly created vhost directory and install WordPress with git.
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd $ cd my-wp
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd/my-wp $ git clone https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress wordpress.git
How does the directory structure look after installation:
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd/my-wp $ tree -L 1
.
└── wordpress.git
1 directory, 0 files
4. Symlink webroot¶
Symlinking the actual webroot directory to htdocs is important. The web server expects every
project’s document root to be in <vhost dir>/htdocs/. This is the path where it will serve
the files. This is also the path where your frameworks entrypoint (usually index.php) should
be found.
Some frameworks however provide its actual content in nested directories of unknown levels. This would be impossible to figure out by the web server, so you manually have to symlink it back to its expected path.
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd/my-wp $ ln -s wordpress.git/ htdocs
How does the directory structure look after symlinking:
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd/my-wp $ tree -L 1
.
├── wordpress.git
└── htdocs -> wordpress.git
2 directories, 0 files
As you can see from the above directory structure, htdocs is available in its expected
path and points to the frameworks entrypoint.
Important
When using Docker Toolbox, you need to explicitly allow the usage of symlinks. See below for instructions:
- Docker Toolbox and Symlinks
5. Add MySQL Database¶
devilbox@php-7.0.20 in /shared/httpd/my-wp $ mysql -u root -h 127.0.0.1 -p -e 'CREATE DATABASE my_wp;'
6. DNS record¶
If you have Auto DNS configured already, you can skip this section, because DNS entries will be available automatically by the bundled DNS server.
If you don’t have Auto DNS configured, you will need to add the following line to your
host operating systems /etc/hosts file (or C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc on Windows):
127.0.0.1 my-wp.loc
7. Open your browser¶
Open your browser at http://my-wp.loc or https://my-wp.loc and follow the installation steps.
(1/7) Choose your desired WordPress language
(2/7) Read pre-installation information
Wordpress installation: Overview
(3/7) Setup database connection
Important
Choose 127.0.0.1 as the database host
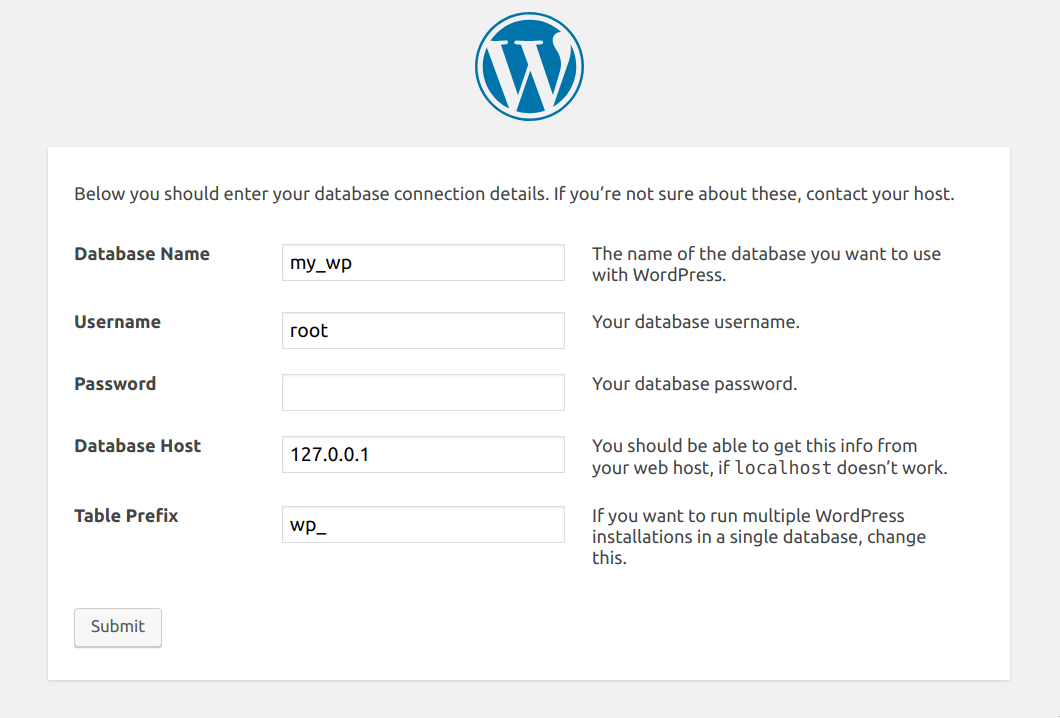
Wordpress installation: Setup database
(4/7) Database setup post screen
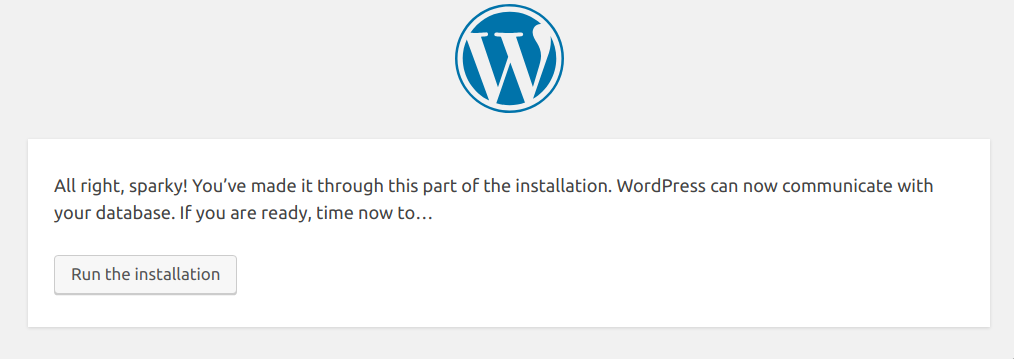
Wordpress installation: Database setup finished
(5/7) Start WordPress installation
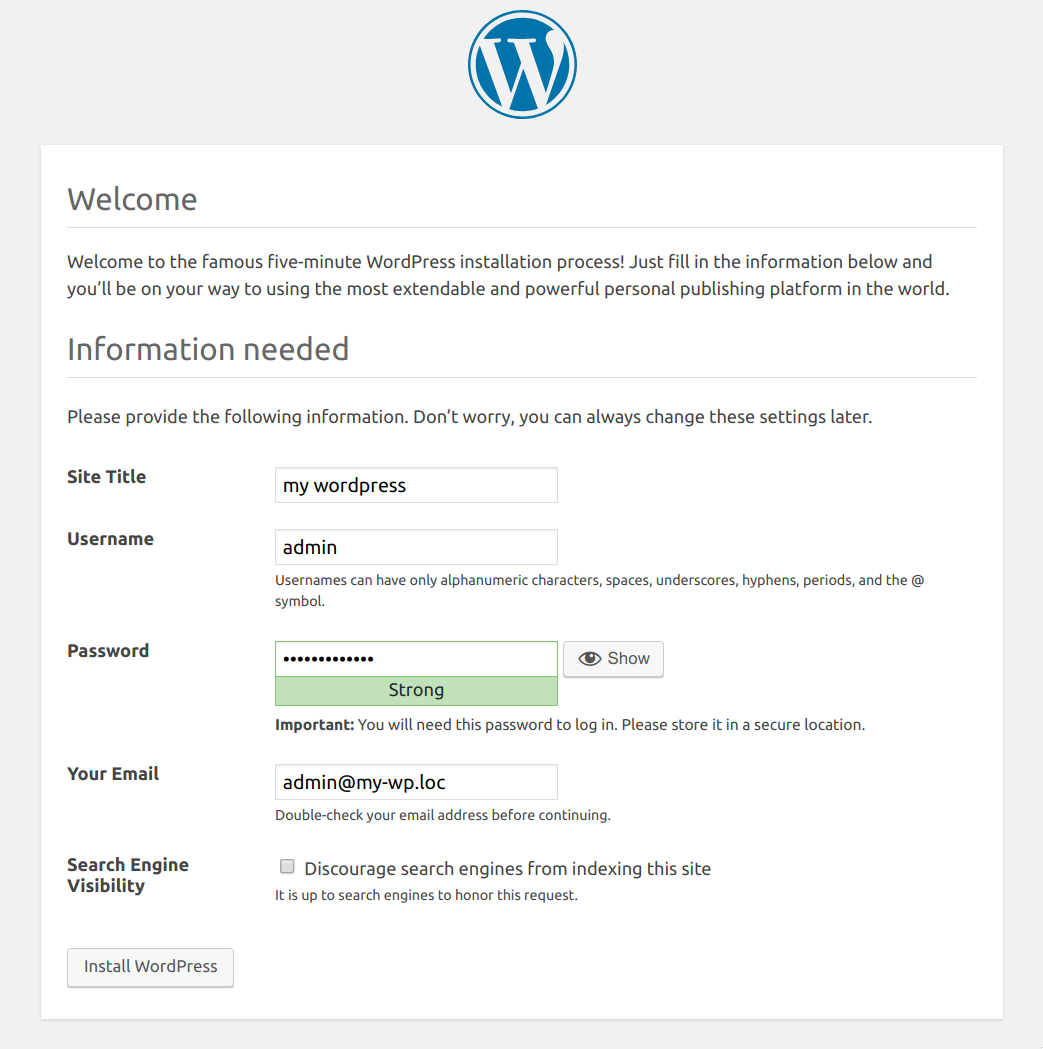
Wordpress installation: Installation
(6/7) Installation success view
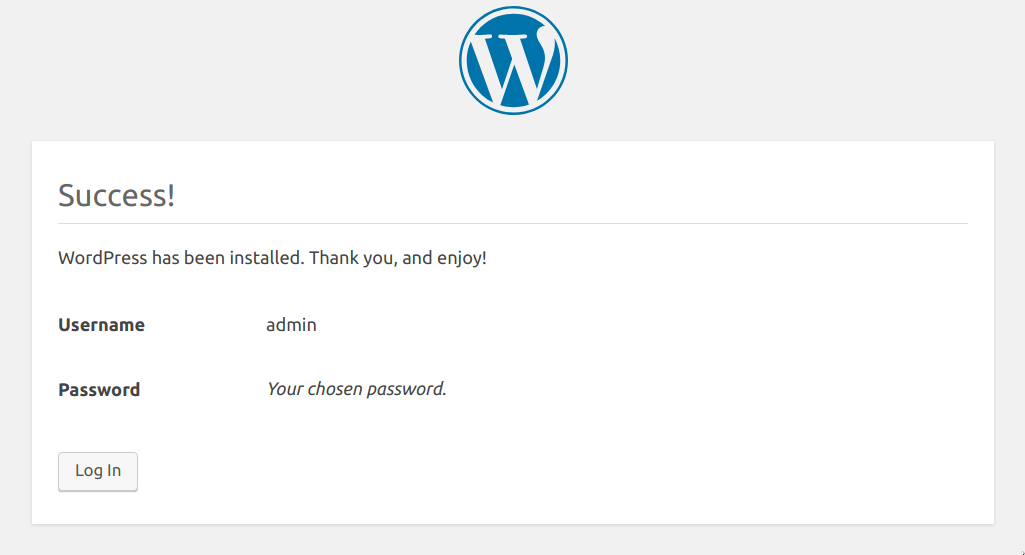
Wordpress installation: Installation finished
(7/7) Login to Admin panel
Next steps¶
Once everything is installed and setup correctly, you might be interested in a few follow-up topics.
Use bundled batteries¶
The Devilbox ships most common Web UIs accessible from the intranet.
Enhance the Devilbox¶
Go ahead and make the Devilbox more smoothly by setting up its core features.
Add services¶
In case your framework/CMS requires it, attach caching, queues, database or performance tools.